Numerische Strömungsmechanik (CFD)
Wir verwenden CFD-Simulationen, um verschiedene komplexe Strömungs-Probleme zu verstehen, zu analysieren und zu lösen.
Die verschiedenen Parameter (wie Druck, Temperatur, Geschwindigkeit, Volumenanteil, usw.) können berechnet werden, um die Leistungsmerkmale (wie Mischeffizienz, Partikeltransport, Rückströmungszonen, usw.) verschiedener Produktdesigns zu evaluieren. Dies kann leicht durch Plot-Optionen wie Konturen, Stromlinien, Schnitte, Partikelflüsse und Iso-Flächen visualisiert werden, um schnell nützliche Einblicke zu liefern und Lösungen zur Designoptimierung aufzuzeigen.
Finite-Elemente-Methode (FEM)
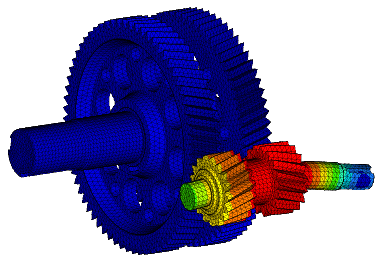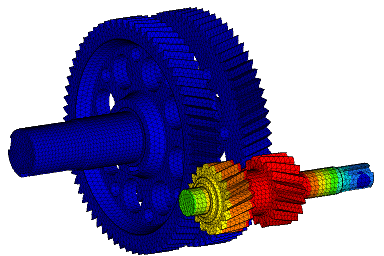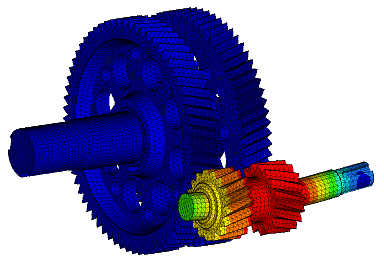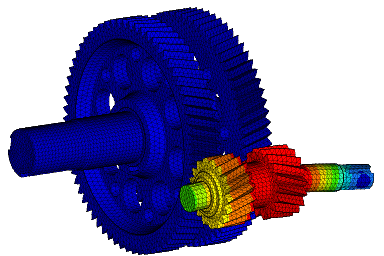
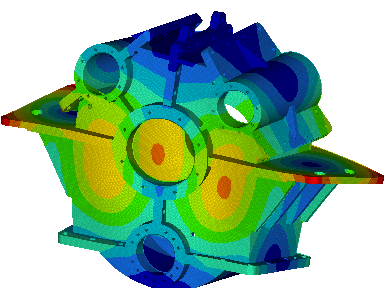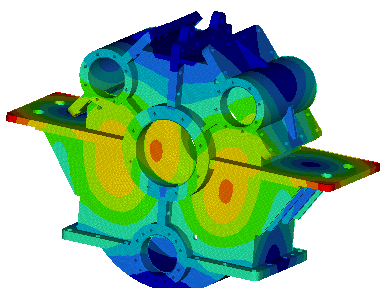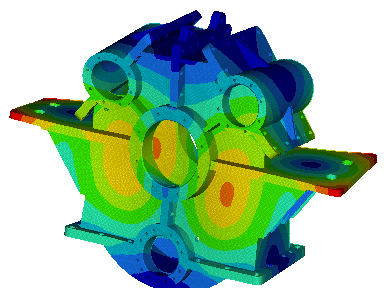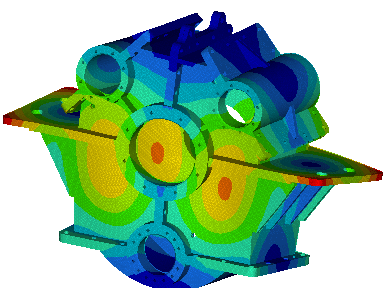
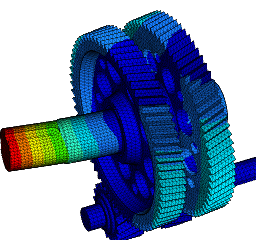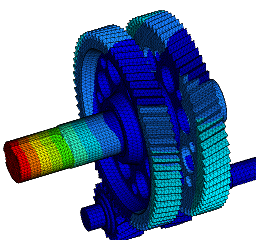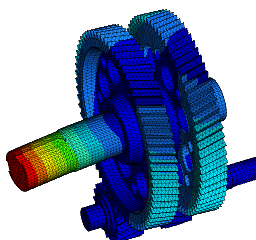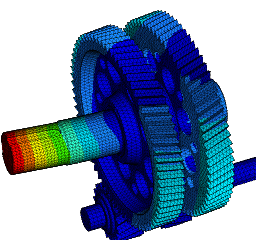

Wir führen FEM-Berechnungen durch, um das strukturelle Verhalten eines Produkts zu bewerten, und führen komplexe Analysen für fortschrittliche Materialien wie kohlefaserverstärkte Kunststoffe (CFK) und Metallmatrix-Verbundwerkstoffe (MMC) durch, um verschiedene komplexe Phänomene wie Nachbeulen, thermische Spannungen, Versagen von Fügestellen, Betriebsfestigkeit, Rissausbreitung usw. zu untersuchen.
Eine Strukturanalyse ermöglicht es:
- das Verhalten komplexer physikalischer Systeme mit Hilfe spezifischer Berechnungscodes zu simulieren (Pre- und Post-Processing, thermische Analysen, Optimierungen);
- die Vorhersage der Lebensdauer zur Bewertung der Zuverlässigkeit verschiedener Komponenten mittels Struktursimulationen;
- mit Hilfe thermomechanischer Simulationen zu erkennen, wie ein Material Wärme leitet oder isoliert, wie ein Festkörper auf eine thermische Belastung reagiert oder wie eine zunehmende Druckbelastung Temperaturänderungen in einem Festkörper verursacht;
- die Vorhersage von Resonanzen und des vibroakustischen Verhaltens während des Betriebs.
Randelementmethode (BEM)
Im Engineering werden die numerische Modellierung und Simulation häufig zur Lösung komplexer Probleme eingesetzt.
Der BEM-Ansatz ist in dieser Hinsicht sehr interessant, da er es ermöglicht, zahlreiche Probleme zu lösen, insbesondere solche, die die Verwendung von Differentialgleichungen erfordern.
Die Methode basiert auf der Diskretisierung des Lösungsbereichs nur an den Grenzen, wodurch die Größe des Problems reduziert und somit die erforderlichen Eingabedaten vereinfacht werden.
Sie basiert auf der Auflösung einer Integralgleichung, die am Rand definiert ist, und nicht auf der direkten Auflösung von partiellen Differentialgleichungen wie bei der FEM.
Bei der BEM wird die Ausgangsgleichung durch eine Integralgleichung umformuliert, die am Rand des Gebiets definiert ist (BIE - Boundary Integral Equation), und ein Integral, das die Lösung am Rand mit der Lösung in den inneren Punkten korreliert.
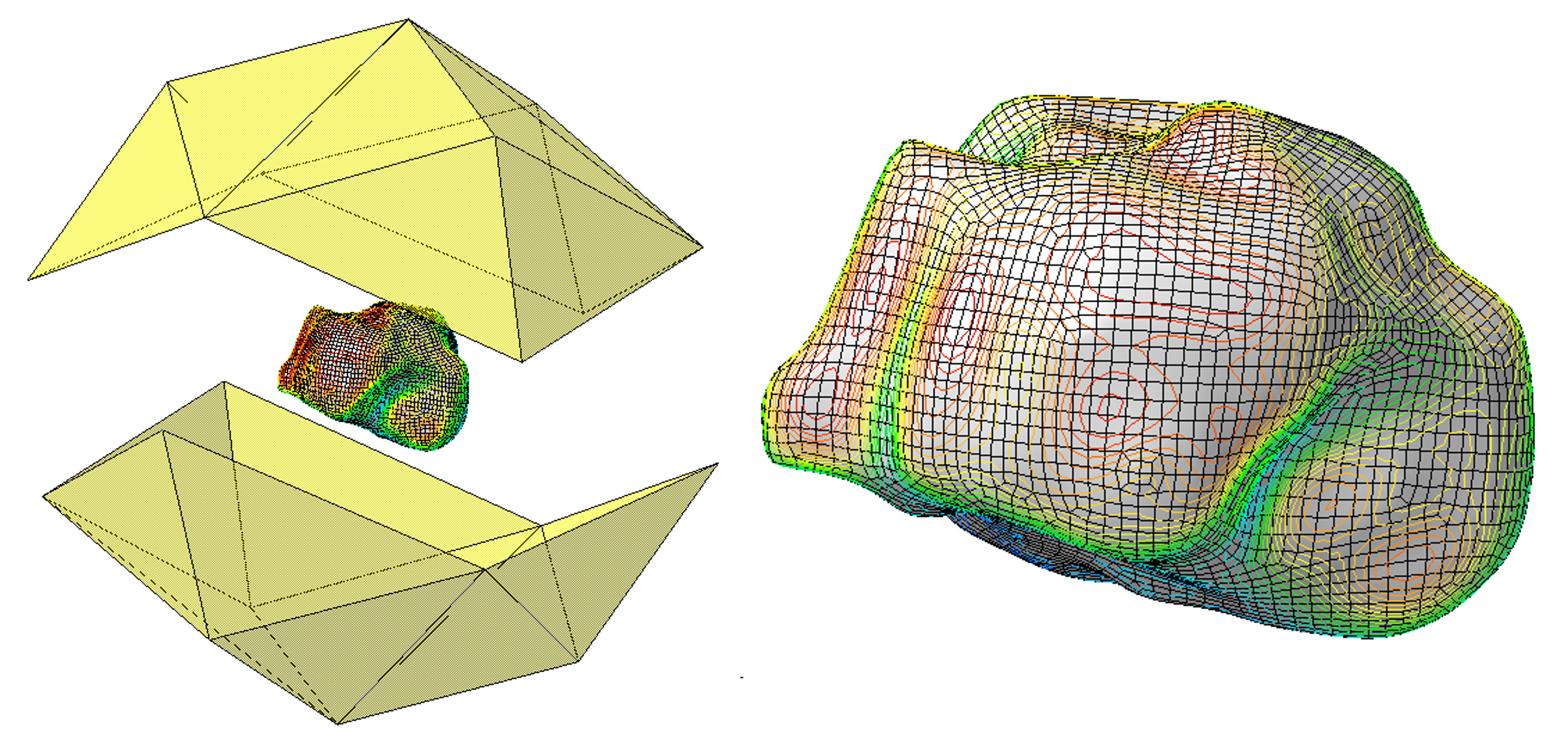
Die Randelementmethode kann in großem Umfang zur Lösung eingesetzt werden:
- bei elektromagnetischen Problemen im Zusammenhang mit elektrischen Maschinen;
- bei Problemen der Luftschallemissionen, Bruchmechanik, Strömung um ein Tragflächenprofil;
- bei Problemen im Zusammenhang mit den Eigenfrequenzen des Schwappens von Flüssigkeiten in Tanks;
- bei Problemen im Zusammenhang mit Kontaktstellen, insbesondere im Zusammenhang mit der Simulation von Klebeverbindungen;
- bei allen Problemen, bei denen es möglich ist, eine Integralgleichung zu definieren.
FEM / BEM – Unterschiede und Vorteile
Vorteile der BEM:
Die Hauptvorteile dieser Methode liegen in der Einfachheit des Aufbaus eines 3D-Modells, bei dem nur die Oberfläche des Körpers diskretisiert werden muss, in der hohen Genauigkeit bei Berechnungen, bei denen die Ergebnisse am Rand im Vergleich zu denen im Inneren von überwiegender Bedeutung sind, sowie in der Anpassungsfähigkeit an Probleme mit offenen oder beweglichen Rändern.
Vorteile der FEM:
Typische Vorteile der FEM liegen in der Einfachheit der Lösung nichtlinearer Probleme und in der Vielseitigkeit, mit der sie auf instationäre Probleme erweitert werden kann.
Vorteile von sowohl BEM als auch FEM:
Es ist vorteilhaft, die Ergebnisse durch den Vergleich der beiden verschiedenen Methoden zu überprüfen.
Multi-objektive parametrische Optimierung
Dank fortschrittlicher Optimierungsalgorithmen können wir Konstruktionsansätze ermitteln, indem ein definierter Konstruktionsumfang durchsucht wird nach einer Kombination von Konstruktionsparametern, die eine Produktoptimierung zulassen, und gleichzeitig die Produktions- und Kostenvorgaben erfüllen.
Wir verwenden Software für die multi-objektive Optimierung, um die beste Kombination von Konstruktionsparametern zu ermitteln, um das gewünschte Leistungsniveau zu erreichen und gleichzeitig den Anforderungen und Randbedingungen gerecht zu werden.
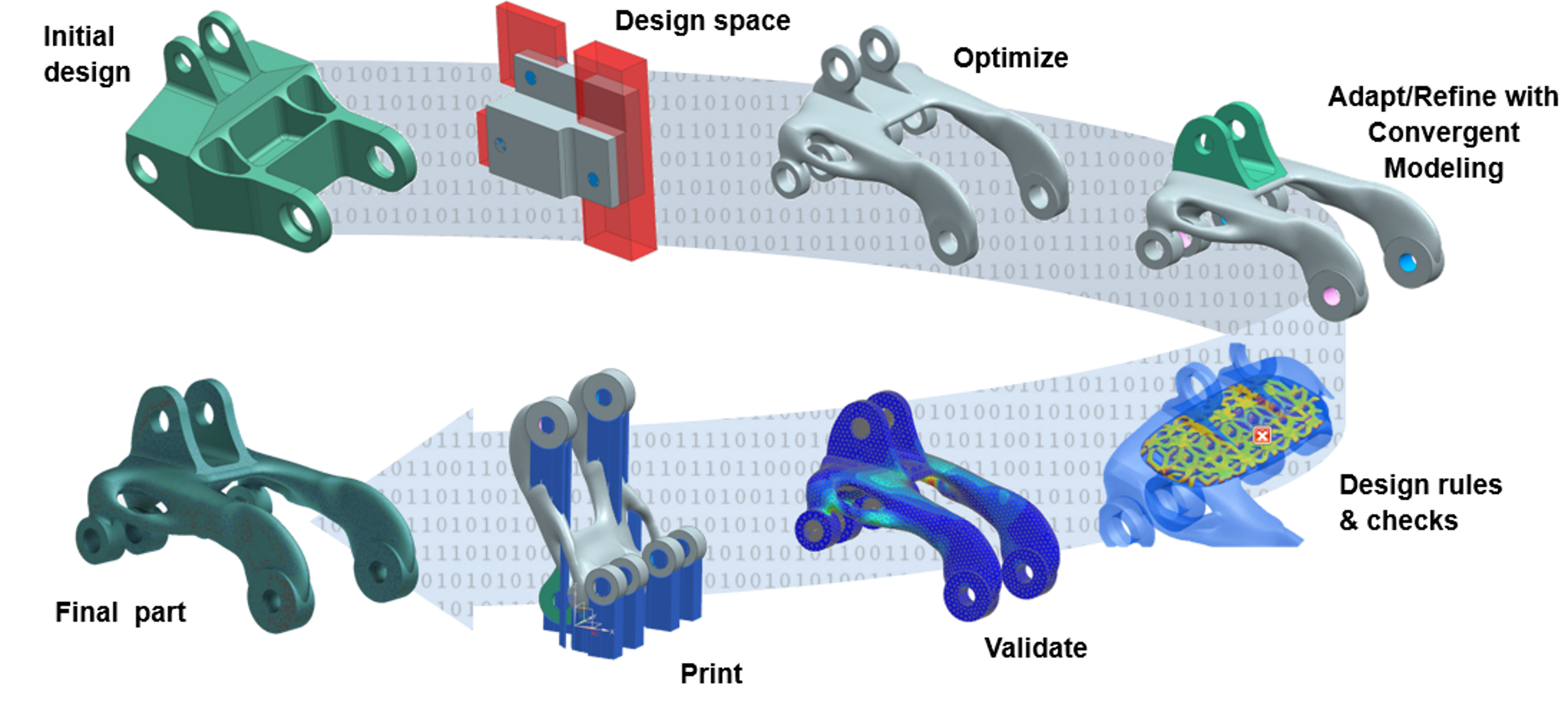
Topologie-Optimierung
Mit herkömmlichen Struktursimulationen können Ingenieure überprüfen, ob eine Konstruktion die erforderlichen Lasten tragen kann.
Durch die topologische Optimierung ist es möglich, diesen Prozess zu verbessern, indem Lasten und Randbedingungen als Eingabe verwendet werden, um ein neues, leichteres Design in einem bereits definierten Volumen zu generieren und strukturell effiziente und leichtgewichtige Konzepte sowohl in der Entwicklungs- als auch in der Redesign-Phase zu definieren.
Dank dieser mathematischen Methode ist es möglich, Gewicht, Fertigungskosten und -zeiten hinsichtlich der funktionalen und mechanischen Anforderungen zu reduzieren.
 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  English (UK)
English (UK) 



